News
What is a Valve Bag
Date:
2024-7-13
Valve Bag: An Overview
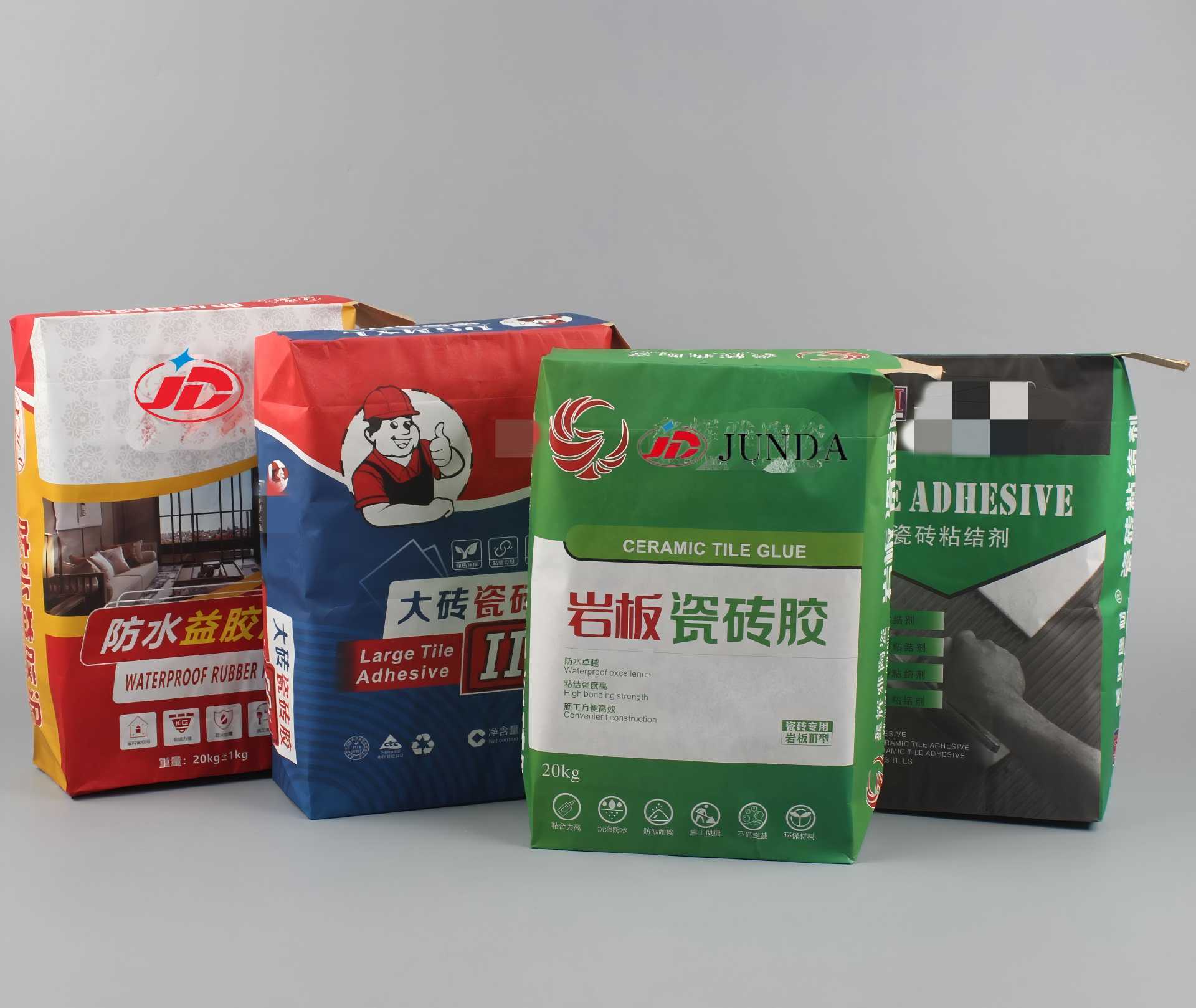
Valve bag are a common type of industrial packaging bag widely used for powdery and granular materials (e.g., cement, fertilizer, animal feed, and chemical raw materials).
1. What is a Valve Bag?
A valve bag is a bag with a sealed bottom and a valve (filling spout) at the top. Its key feature is that materials are filled through the valve, which automatically closes after filling—eliminating the need for sewing or heat sealing. This design ensures excellent sealing performance, making it ideal for automated production lines.
2. Key Structural Features
2.1Valve Design: The top of the bag has a foldable valve (made of paper or PE) that opens during filling and closes automatically afterward.
2.2No Additional Sealing Required: Unlike traditional bags that require sewing or heat sealing, valve sacks rely on the self-sealing valve.
2.3Diverse Materials: Commonly used materials include kraft paper, PP woven fabric, PE film, or composite materials (e.g., laminated woven fabric, multi-layer kraft paper).
3. Common Types
3.1Paper Valve Bag: Made of kraft paper, recyclable and eco-friendly, often used for cement, flour, etc.
3.2Woven Valve Bag: PP (polypropylene) woven fabric with PE liner, moisture-proof and wear-resistant, suitable for fertilizers and animal feed.
3.3Multi-layer Composite Valve Bag: Combine paper, aluminum film, etc., offering anti-static and moisture-proof properties for high-demand chemical products.
4. Working Principle
During filling, the material is fed through a nozzle inserted into the valve. The filling pressure expands the valve, and once filling is complete, the nozzle retracts, allowing the valve to close automatically due to material elasticity or folding design, preventing leaks.
5. Advantages
5.1High-Speed Filling: Compatible with automated equipment, reaching speeds of 1,000–2,000 bags/hour.
5.2Leak-Proof & Sealed: Prevents dust and moisture ingress, ideal for long-distance transport.
5.3Labor-Saving: Eliminates additional sealing steps.
5.4Eco-Friendly: Some materials are biodegradable or recyclable (e.g., kraft paper).
6. Applications
6.1Construction Industry: Cement, gypsum powder, putty powder.
6.2Agriculture: Fertilizers, animal feed, seeds.
6.3Chemicals: Plastic pellets, pigments, powdered additives.
6.4Food Industry: Flour, starch, sugar (requires food-grade materials).